💡Important for You
WEGOVITA offers medical coordination services by connecting international patients with top hospitals and specialists across Germany. We support access to expert evaluations, facilitate treatment logistics, and present a range of available medical options.
However, WEGOVITA does not provide direct medical treatment, make medical diagnoses, or recommend specific therapies. All final medical decisions—including diagnosis, treatment planning, and cost—are made solely by licensed medical professionals after a full clinical assessment of the individual patient.
This information is provided for informational purposes, based on internationally recognized guidelines and practices used in Germany’s leading medical institutions. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice.
💡 Interested in clinical trial references, treatment innovations, or cost comparisons? Contact our medical coordination team at info@wegovita.com for personalized assistance.
Your Health. Your Journey. With WEGOVITA.



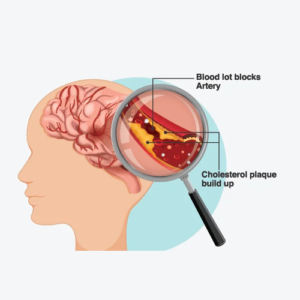
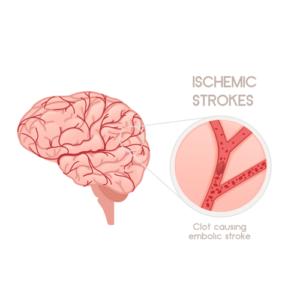
 1. Causes & Risk Factors of Ischemic Stroke
1. Causes & Risk Factors of Ischemic Stroke A. Primary Causes of Ischemic Stroke
A. Primary Causes of Ischemic Stroke
 Non-Contrast CT Scan (NCCT) – First-line imaging to differentiate between ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke.
Non-Contrast CT Scan (NCCT) – First-line imaging to differentiate between ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke.